Many people notice changes in their leg veins as they age, but not all vein conditions are the same. Spider veins and varicose veins represent two distinct vascular conditions that affect millions of people worldwide. While both involve problems with blood circulation in the legs, they differ significantly in appearance, symptoms, and treatment approaches. Here is more information on the key distinctions between spider veins and varicose veins:
Exploring Spider Veins
Spider veins, medically known as telangiectasias, are small, thin blood vessels that become visible beneath the skin’s surface. These tiny veins typically measure less than 1 millimeter in diameter and appear as red, blue, or purple web-like patterns on the legs, face, or other body areas. These veins develop when small valves inside the veins weaken or become damaged. When these valves fail to function properly, blood pools in the vessel, causing it to enlarge and become visible through the skin.
These superficial veins usually cause minimal physical discomfort. Most people report no pain, though some may experience mild burning, itching, or heaviness in the affected area. The primary concern for many individuals with this condition is cosmetic, as the visible patterns can affect confidence and clothing choices.
Understanding Varicose Veins
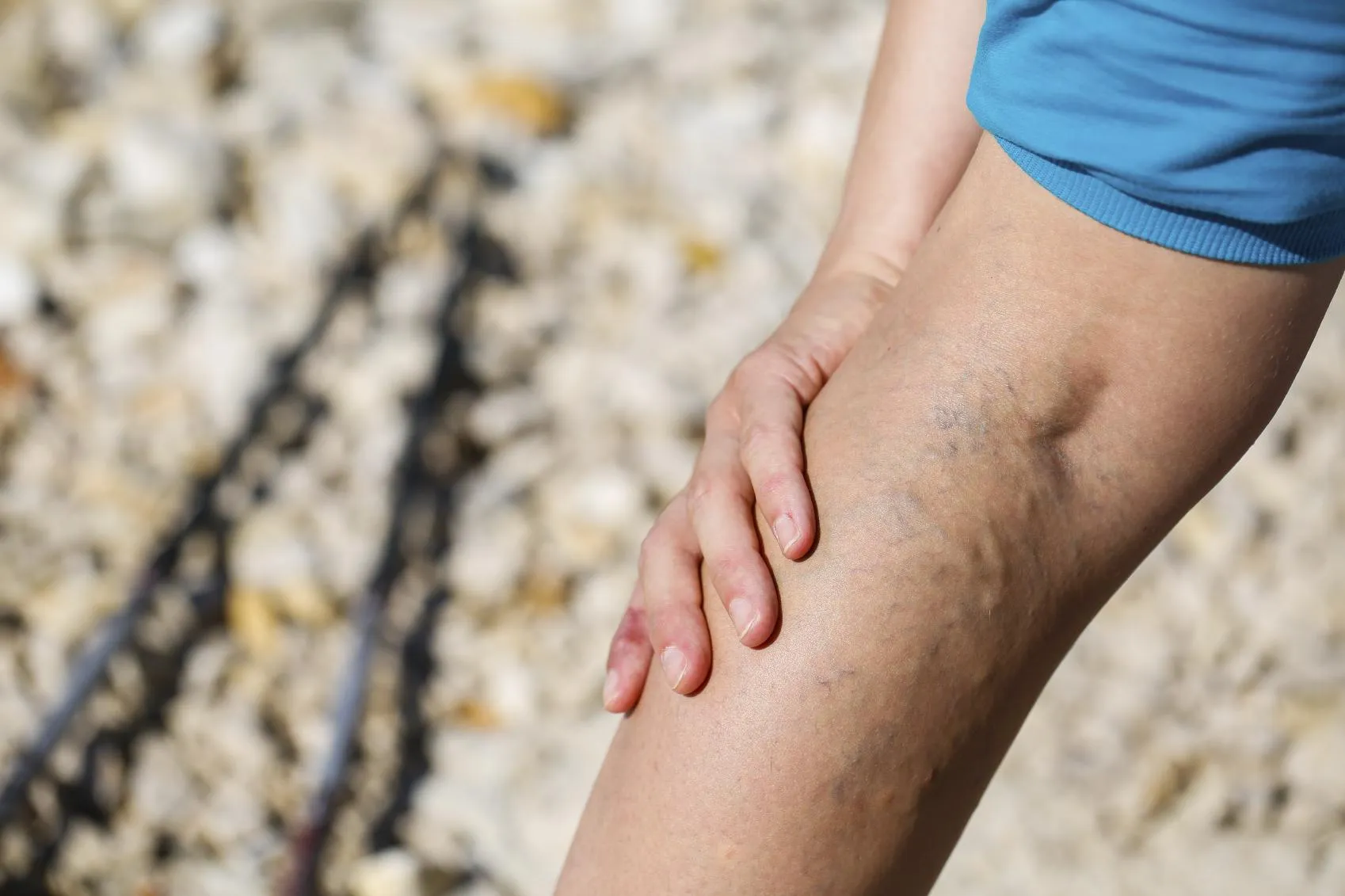
Varicose veins are larger, swollen blood vessels that bulge above the skin’s surface. These veins typically measure 3 millimeters or more in diameter and appear as twisted, rope-like cords running along the legs. The color ranges from dark blue to purple, and the raised appearance makes them easily distinguishable.
The development of varicose veins follows a similar mechanism but affects deeper, larger vessels. When the valves in these larger veins fail, blood accumulates and causes the vein wall to stretch and bulge outward. This process affects the saphenous veins and their branches, which are the main superficial veins in the legs.
Varicose veins frequently cause more noticeable symptoms. People with varicose veins may experience aching, throbbing, cramping, or a heavy feeling in their legs. These symptoms often worsen after prolonged standing or sitting and may improve with elevation or movement. Some individuals also develop skin changes around varicose veins, including darkening, dryness, or inflammation.
Identifying Key Differences
The most obvious difference between these vein conditions lies in their size and appearance. Spider veins remain flat against the skin and create delicate, web-like patterns, while varicose veins protrude above the skin surface and form thick, twisted cords. Spider veins rarely cause significant discomfort, whereas varicose veins often produce pain, swelling, and other bothersome symptoms.
Treatment options vary based on the type and severity of the vein condition. Spider veins typically respond well to sclerotherapy, a procedure where a solution is injected into the vein to cause it to collapse and fade. Laser therapy offers another effective option for treating these veins, particularly on the face and smaller leg veins.
Varicose vein treatment depends on the size and location of the affected veins. Smaller varicose veins may respond to sclerotherapy. Larger ones might require procedures such as endovenous laser therapy, radiofrequency ablation, or surgical removal. Compression stockings often provide symptom relief for both conditions and may slow progression.
Find a Vein Specialist
Both types of veins result from similar underlying problems with vein valve function, but they manifest differently and require tailored treatment approaches. Spider veins primarily present cosmetic concerns with minimal symptoms. Varicose veins often cause discomfort and may lead to complications if left untreated. Understanding the differences between these veins empowers you to make informed decisions about your vascular health and seek appropriate care when needed.