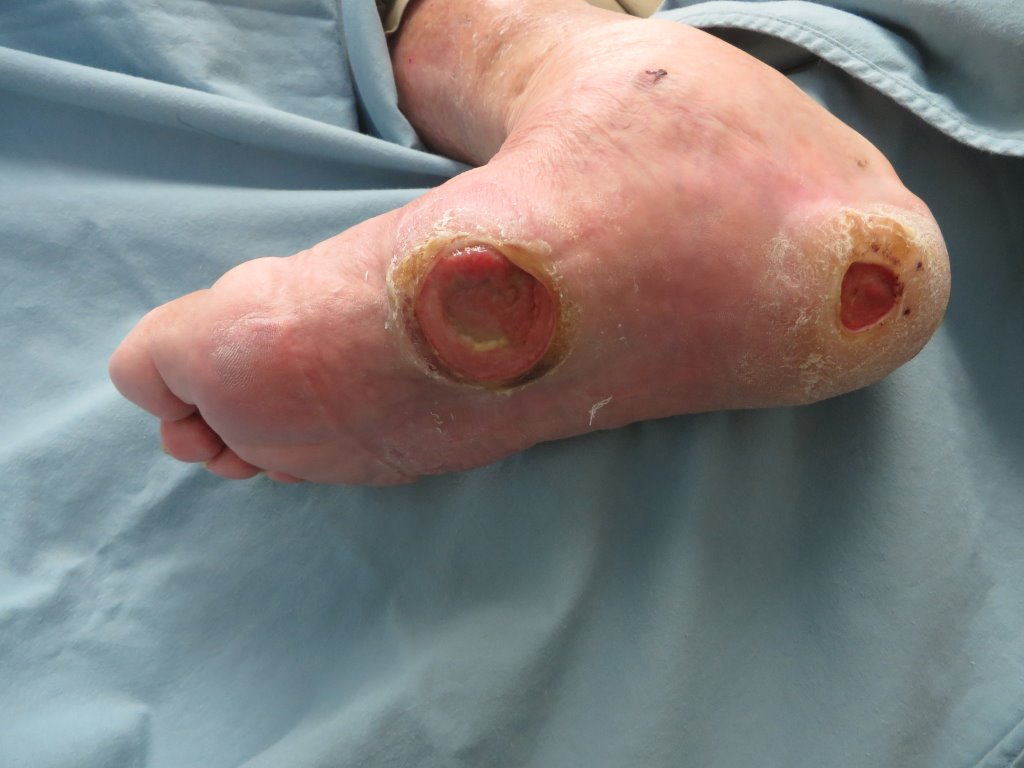
Diabetes affects millions of people worldwide and can lead to various complications throughout the body. One of the most serious complications involves the development of foot ulcers, which occur in approximately 15% of people with diabetes. Understanding this relationship helps recognize risk factors, implement preventive measures, and seek appropriate diabetic wound care when needed.
Impacting Circulation and Nerve Function
Diabetic wound care is usually needed to treat ulcers caused by diabetes. Diabetes causes elevated blood glucose levels over extended periods, which damages blood vessels and nerves throughout the body. The feet are particularly vulnerable to these changes due to their distance from the heart and their role in supporting body weight. High blood sugar levels damage the inner lining of blood vessels, leading to reduced blood flow to the extremities.
Diabetic neuropathy represents another significant factor in foot ulcer development. This condition occurs when elevated glucose levels damage nerve fibers, particularly those in the feet and legs. The damage manifests in two primary ways: loss of sensation and autonomic nerve dysfunction.
Sensory neuropathy reduces the ability to feel pain, temperature, and pressure in the feet. This loss of protective sensation means that minor injuries, pressure points, or irritation from ill-fitting shoes may go unnoticed. Without the warning signals that pain typically provides, small wounds can worsen and develop into ulcers.
Exploring Risk Factors
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing diabetic foot ulcers. Duration of diabetes plays a significant role, as longer exposure to elevated blood glucose levels increases the risk of complications. Poor glycemic control accelerates the damage to blood vessels and nerves, heightening ulcer risk.
Foot deformities, such as bunions, hammertoes, or prominent bone structures, create pressure points that can lead to tissue breakdown. These structural abnormalities often develop over time and may be exacerbated by diabetic complications. Previous foot ulcers or amputations indicate a higher risk for future ulcers. The presence of calluses or corns also signals areas of repeated pressure that may progress to ulceration without proper management.
Kidney disease, which commonly occurs alongside diabetes, can affect healing and increase infection susceptibility. Vision problems may prevent individuals from detecting early signs of foot problems during self-examination. Smoking further reduces blood circulation, while inadequate foot care practices, such as improper nail trimming or walking barefoot, increase injury risk.
Identifying Management Strategies
Managing diabetes effectively forms the foundation of foot ulcer prevention. Maintaining blood glucose levels within target ranges helps slow the progression of diabetic complications and supports the body’s natural healing processes. Daily foot inspection allows for early detection of problems before they progress to ulcers. This involves checking for cuts, bruises, swelling, redness, or changes in skin color and texture.
Proper footwear selection protects feet from injury and pressure points. Shoes should fit properly, provide adequate support, and accommodate any foot deformities. Avoiding walking barefoot reduces the risk of cuts and puncture wounds.
Professional foot care through regular podiatric examinations helps identify and address risk factors before problems develop. Healthcare providers can assess circulation, test sensation, and provide specialized treatments for conditions like calluses or ingrown toenails. Wound care protocols become necessary when minor injuries occur. Cleaning wounds promptly, applying appropriate dressings, and monitoring for signs of infection help prevent progression to more serious complications.
Learn About Diabetic Wound Care
The relationship between diabetes and foot ulcers highlights the need for proactive management and regular monitoring. Early recognition of risk factors, combined with appropriate preventive measures, significantly reduces the likelihood of developing serious complications. Taking these steps helps maintain foot health and overall quality of life for individuals living with diabetes.